The singlet and triplet carbene is the topic of Chapter 4, especially sections 1 and 2. The ground state of methylene is the triplet, with one electron in the σ-orbital and one electron in the π-orbital, with the spins aligned. The lowest singlet state places the pair of electrons in the σ-orbital, and this state is about 9 kcal mol-1 higher in energy than the triplet. The next lowest singlet state has one electron in each of the σ- and π-orbitals, with the spins aligned. The singlet state with both electrons in the π-orbital is the highest of these four states, some 60 kcal mol-1 above the ground state triplet.
Hoffmann and Borden now pose the question “Can the doubly occupied π carbene (1A1-σ0π2) be the ground state with appropriate substitution?” The answer they find is yes!1
The trick is to find a combination of substituents that will raise the energy of the σ-orbital and lower the energy of the π-orbital. The latter effect can be enhanced if the π-orbital can be a part of an aromatic (6e–) ring.
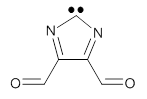
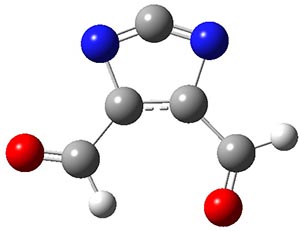
Two of the best possibilities for identifying a ground state 1A1-σ0π2 carbene are 1 and 2. The CASSCF/6-31G(d) optimized geometries of these two are shown in Figure 1. In 1, the nitrogen lone pairs act to destabilize the σ-orbital, while the aldehyde group acts as a withdrawing group to stabilize the π-orbital. The result is that the 1A1-σ0π6 state of 1 is predicted to be about 8 kcal mol-1 more stable than the triplet state, as per CASPT2 and CCSD(T) computations.
|
|
|
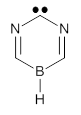
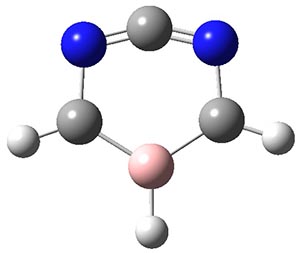
An ever greater effect is predicted for 2. Here the nitrogen lone pairs adjacent to the carbene act to destabilize the σ-orbital. The empty π-orbital on B lowers the energy of the carbene π-orbital by making it part of the 6-electron aromatic ring. The 1A1-σ0π6 state of 2 is predicted to be about 25 kcal mol-1 more stable than its triplet state!
|
1 |
2 |
Figure 1. CASSCF/6-31G(d) optimized geometries of the 1A1-σ0π6 states of 1 and 2.
References
(1) Chen, B.; Rogachev, A. Y.; Hrovat, D. A.; Hoffmann, R.; Borden, W. T. "How to
Make the σ0π2 Singlet the Ground State of Carbenes," J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13954-13964, DOI: 10.1021/ja407116e.
InChIs
1: InChI=1S/C5H2N2O2/c8-1-4-5(2-9)7-3-6-4/h1-2H
InChIKey=QDSVROXEBBWIOO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
2: InChI=1S/C3H3BN2/c1-4-2-6-3-5-1/h1-2,4H
InChIKey=MQJXDZBYOSOLST-UHFFFAOYSA-N

Henry Rzepa responded on 14 Oct 2013 at 12:42 pm #
Is e.g. 2 really a surprise? Take for example the crystal structure for molecule reported in doi: 10.1021/ja052987g. This can be drawn as a N2C: carbene, stabilised by aromatic delocalisation of the type noted above. The crystal structure reference is KARZUZ.
Another series of this type were suggested a few years back, doi;10.1039/B003971N as potential Möbius aromatics, based on promoting or demoting an electron pair from/to a carbene.
Perhaps an updated trawl of the crystal structure database might be considered a useful adjunct to theoretical speculation of this type; it might even reveal real examples! IMHO, not enough people search the CCDC for examples of hypothesized molecules!
Henry Rzepa responded on 15 Oct 2013 at 12:46 am #
PS, I now appreciate that KARZUZ is not after all analogous to 2, since a different type of electron redistribution and counting is occurring. Compound 2, as shown in the Jmol graphic above, has nominally an allene type central carbon, where the two π-bonds would be twisted (hence my analogy to Möbius systems). The molecule is in fact computed flat, but the C=N bond length is nevertheless very short (1.22Å), which is why the rendering program used shows it as double. Certainly subtle.
Henry Rzepa responded on 18 Oct 2013 at 5:49 am #
More pondering about the structure of 2 (and calculation) reveals quite unusual features.
Thus the Wiberg bond order indices of the N=C=C bonds are 1.79, and the Wiberg bond index at the central carbon is 3.8. The other N-C bonds have a bond order of ~1.22 and the C-B bonds 1.30. This does conform to the structure of 2 shown by Steve above. But that allene-like motif should be twisted! And the system is computed as planar!
But another resonance form can be formulated which reveals a classical aromatic ring, and a vinyl carbocation for the top carbon, and this in turn implies a zwitterionic resonance with a negative charge on the B. That should display lower bond orders for the N–C–N region, more typical of that of benzene, and presumably a large dipole moment. In fact, its computed as ~1.2D, and the system is scarcely solvated by eg water (you would expect a vinyl cation to be solvated).
One might also assume that the system would have interesting Lewis-acid properties, since it could bind a Lewis base without disrupting the aromaticity.
Six vs ten aromatic electrons? « Henry Rzepa responded on 20 Oct 2013 at 8:57 am #
[…] shown below. This example comes from a recently published article[1] which was highlighted on Steve Bachrach’s blog. Here aromaticity has resulted from a slightly different phenomenon, whereby a 4π-electron planar […]